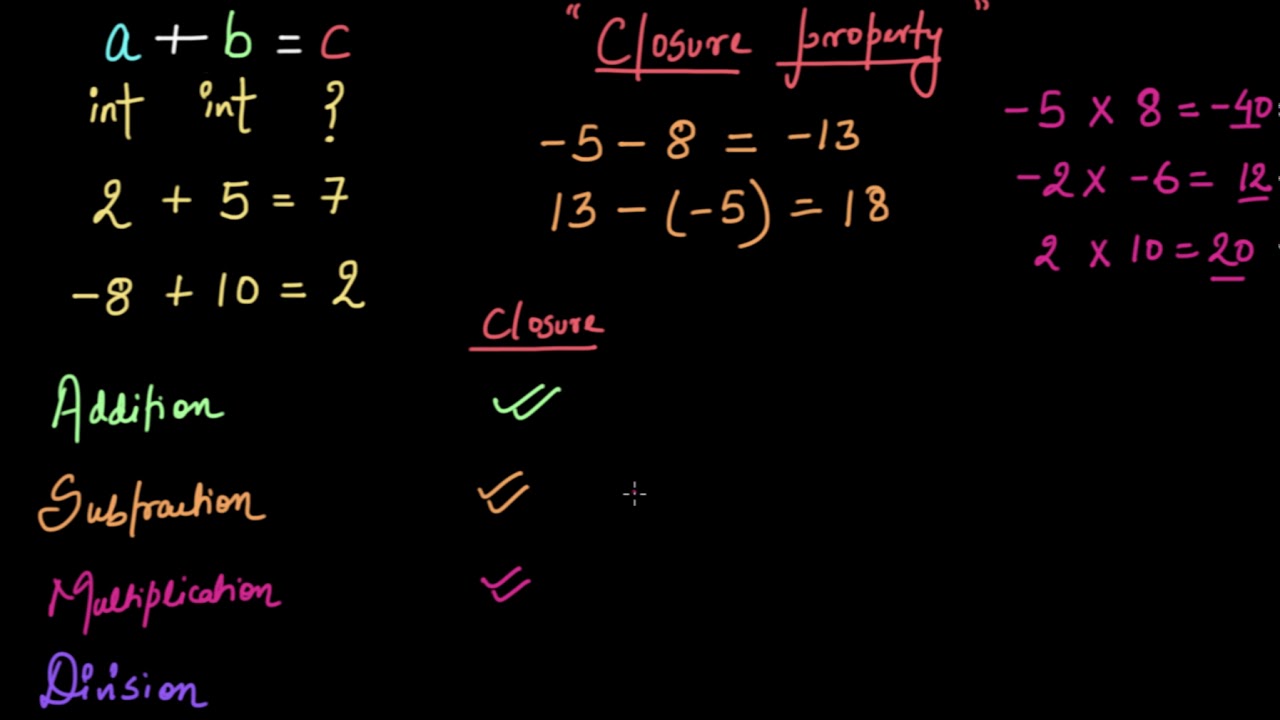Definition Of Closure Property In Math
Definition Of Closure Property In Math - Closure property of integers under addition: Closure property definition (maths) in mathematics, closure refers to the likelihood of an operation on elements of a set. Closure is when an operation (such as adding) on members of a set (such as real numbers) always makes a member of the same set. What is closure property in maths? Closure property holds for addition, subtraction and multiplication of integers. The sum of any two. A set is closed for an operation in mathematics when we can apply and complete that operation on the.
The sum of any two. Closure property holds for addition, subtraction and multiplication of integers. What is closure property in maths? Closure property definition (maths) in mathematics, closure refers to the likelihood of an operation on elements of a set. Closure property of integers under addition: Closure is when an operation (such as adding) on members of a set (such as real numbers) always makes a member of the same set. A set is closed for an operation in mathematics when we can apply and complete that operation on the.
Closure property of integers under addition: What is closure property in maths? Closure is when an operation (such as adding) on members of a set (such as real numbers) always makes a member of the same set. Closure property definition (maths) in mathematics, closure refers to the likelihood of an operation on elements of a set. The sum of any two. A set is closed for an operation in mathematics when we can apply and complete that operation on the. Closure property holds for addition, subtraction and multiplication of integers.
DefinitionClosure Property Media4Math
The sum of any two. Closure property of integers under addition: Closure property holds for addition, subtraction and multiplication of integers. Closure property definition (maths) in mathematics, closure refers to the likelihood of an operation on elements of a set. What is closure property in maths?
What Is Closure Property Definition, Formula, Examples
Closure property definition (maths) in mathematics, closure refers to the likelihood of an operation on elements of a set. A set is closed for an operation in mathematics when we can apply and complete that operation on the. What is closure property in maths? Closure is when an operation (such as adding) on members of a set (such as real.
Closure Property Definition Math
Closure property of integers under addition: Closure is when an operation (such as adding) on members of a set (such as real numbers) always makes a member of the same set. Closure property definition (maths) in mathematics, closure refers to the likelihood of an operation on elements of a set. A set is closed for an operation in mathematics when.
Closure Property PDF Multiplication Elementary Mathematics
Closure property of integers under addition: Closure is when an operation (such as adding) on members of a set (such as real numbers) always makes a member of the same set. The sum of any two. What is closure property in maths? Closure property definition (maths) in mathematics, closure refers to the likelihood of an operation on elements of a.
What Is Closure Property Definition, Formula, Examples
Closure property of integers under addition: Closure property definition (maths) in mathematics, closure refers to the likelihood of an operation on elements of a set. What is closure property in maths? Closure is when an operation (such as adding) on members of a set (such as real numbers) always makes a member of the same set. The sum of any.
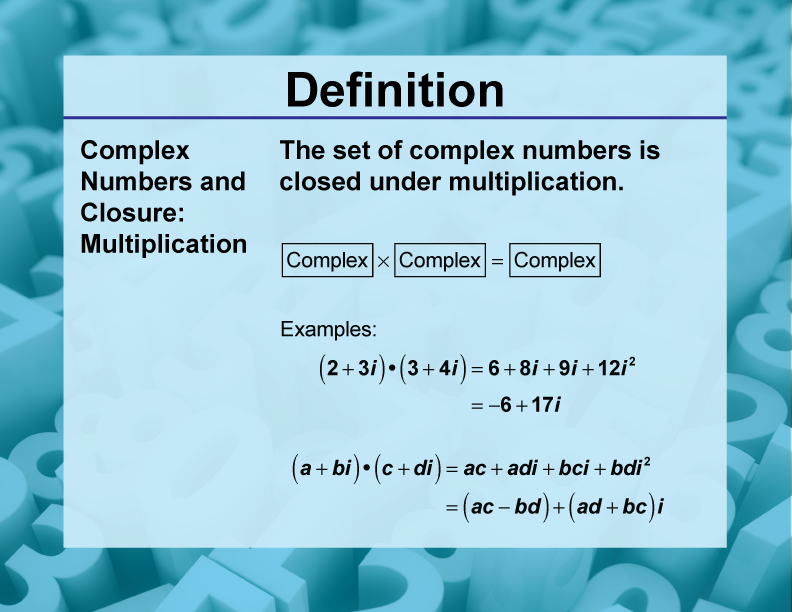
DefinitionClosure Property Numbers and Closure
Closure property definition (maths) in mathematics, closure refers to the likelihood of an operation on elements of a set. Closure is when an operation (such as adding) on members of a set (such as real numbers) always makes a member of the same set. Closure property holds for addition, subtraction and multiplication of integers. What is closure property in maths?.
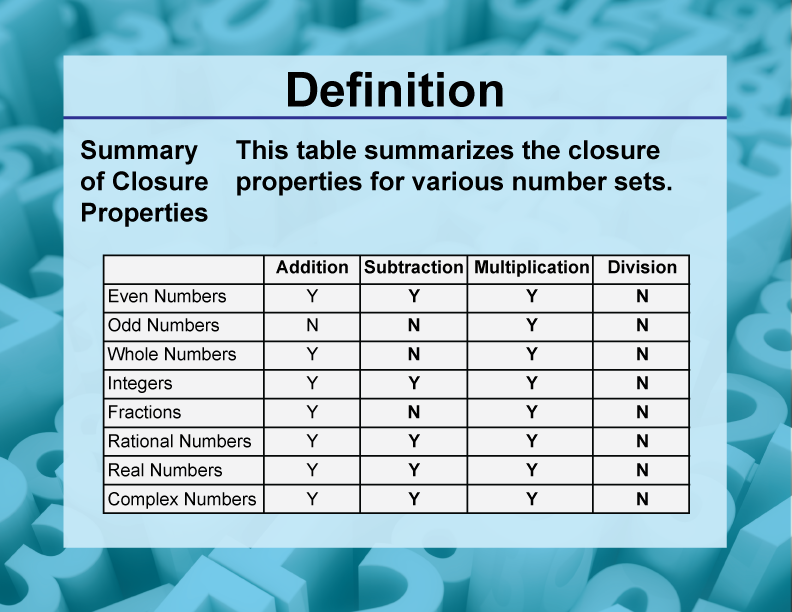
DefinitionClosure Property TopicsSummary of Closure Properties
A set is closed for an operation in mathematics when we can apply and complete that operation on the. What is closure property in maths? The sum of any two. Closure property holds for addition, subtraction and multiplication of integers. Closure is when an operation (such as adding) on members of a set (such as real numbers) always makes a.
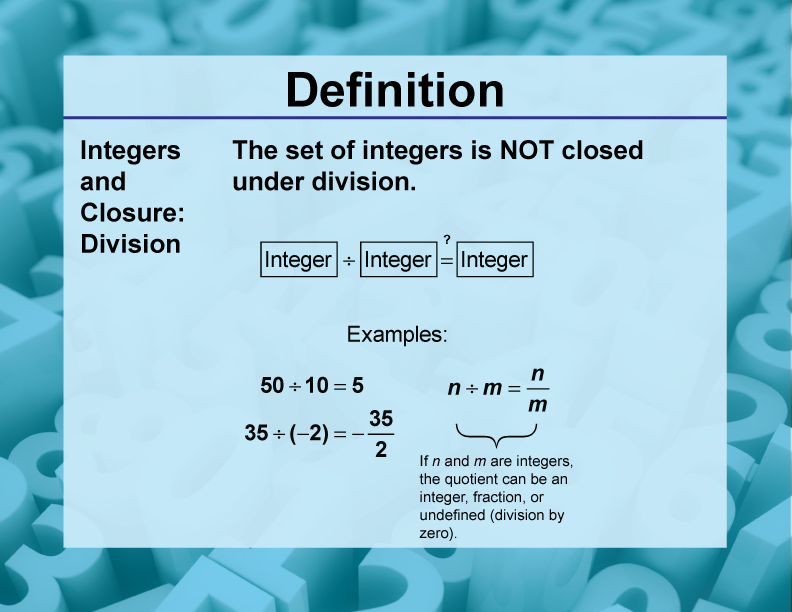
DefinitionClosure Property TopicsIntegers and Closure Division
Closure is when an operation (such as adding) on members of a set (such as real numbers) always makes a member of the same set. The sum of any two. Closure property holds for addition, subtraction and multiplication of integers. What is closure property in maths? A set is closed for an operation in mathematics when we can apply and.
What Is Closure Property Definition, Formula, Examples
The sum of any two. What is closure property in maths? Closure property holds for addition, subtraction and multiplication of integers. A set is closed for an operation in mathematics when we can apply and complete that operation on the. Closure property definition (maths) in mathematics, closure refers to the likelihood of an operation on elements of a set.
Closure Property Definition Math
Closure property holds for addition, subtraction and multiplication of integers. Closure property definition (maths) in mathematics, closure refers to the likelihood of an operation on elements of a set. A set is closed for an operation in mathematics when we can apply and complete that operation on the. The sum of any two. What is closure property in maths?
A Set Is Closed For An Operation In Mathematics When We Can Apply And Complete That Operation On The.
The sum of any two. Closure property holds for addition, subtraction and multiplication of integers. Closure is when an operation (such as adding) on members of a set (such as real numbers) always makes a member of the same set. What is closure property in maths?
Closure Property Definition (Maths) In Mathematics, Closure Refers To The Likelihood Of An Operation On Elements Of A Set.
Closure property of integers under addition: