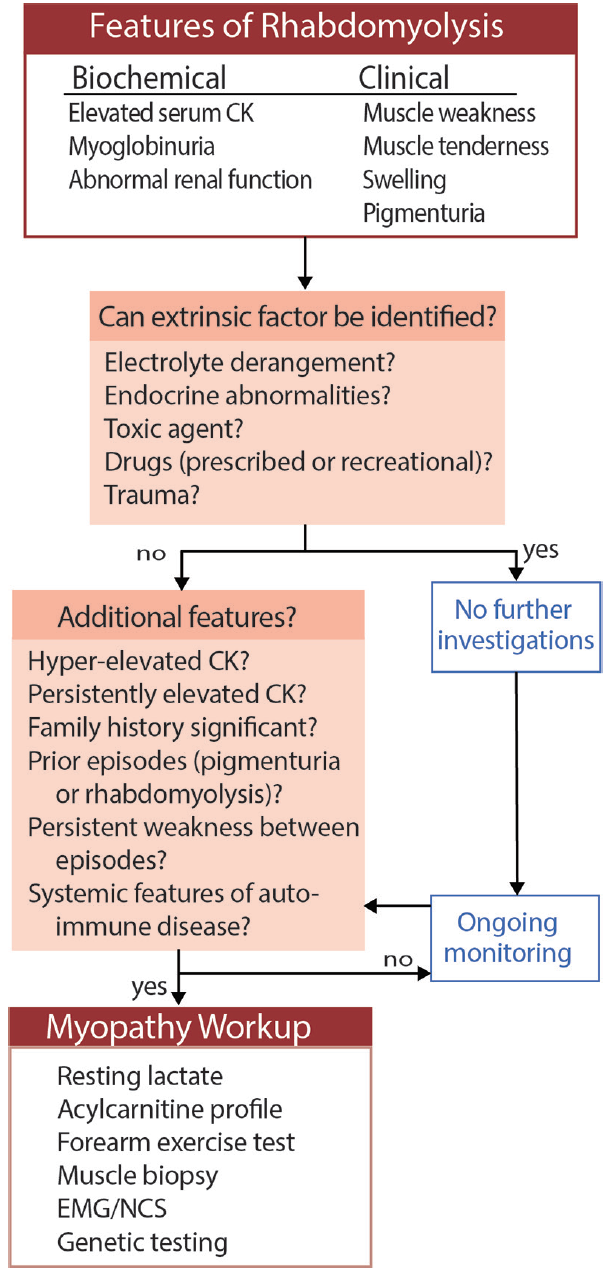
Rhabdomyolysis Discharge Criteria
Rhabdomyolysis Discharge Criteria - The diagnostic criteria for aki include any one or more of the following: This suggests that otherwise healthy patients with uncomplicated rhabdomyolysis and a normal first creatinine who can hydrate themselves orally. Standardize inpatient management of rhabdomyolysis; Establish appropriate admission and discharge criteria for rhabdomyolysis; 1) an increase of serum creatinine by ≥ 0.3 mg/dl (≥ 26.5 μmol/l).
1) an increase of serum creatinine by ≥ 0.3 mg/dl (≥ 26.5 μmol/l). Establish appropriate admission and discharge criteria for rhabdomyolysis; Standardize inpatient management of rhabdomyolysis; The diagnostic criteria for aki include any one or more of the following: This suggests that otherwise healthy patients with uncomplicated rhabdomyolysis and a normal first creatinine who can hydrate themselves orally.
Establish appropriate admission and discharge criteria for rhabdomyolysis; Standardize inpatient management of rhabdomyolysis; This suggests that otherwise healthy patients with uncomplicated rhabdomyolysis and a normal first creatinine who can hydrate themselves orally. 1) an increase of serum creatinine by ≥ 0.3 mg/dl (≥ 26.5 μmol/l). The diagnostic criteria for aki include any one or more of the following:
Neuromuscular Notes Rhabdomyolysis Practical Neurology
Standardize inpatient management of rhabdomyolysis; 1) an increase of serum creatinine by ≥ 0.3 mg/dl (≥ 26.5 μmol/l). The diagnostic criteria for aki include any one or more of the following: This suggests that otherwise healthy patients with uncomplicated rhabdomyolysis and a normal first creatinine who can hydrate themselves orally. Establish appropriate admission and discharge criteria for rhabdomyolysis;
Rhabdomyolysis and secondary renal failure in critically ill surgical
Standardize inpatient management of rhabdomyolysis; Establish appropriate admission and discharge criteria for rhabdomyolysis; The diagnostic criteria for aki include any one or more of the following: This suggests that otherwise healthy patients with uncomplicated rhabdomyolysis and a normal first creatinine who can hydrate themselves orally. 1) an increase of serum creatinine by ≥ 0.3 mg/dl (≥ 26.5 μmol/l).
Classification of complications of rhabdomyolysis according to time
Establish appropriate admission and discharge criteria for rhabdomyolysis; The diagnostic criteria for aki include any one or more of the following: 1) an increase of serum creatinine by ≥ 0.3 mg/dl (≥ 26.5 μmol/l). Standardize inpatient management of rhabdomyolysis; This suggests that otherwise healthy patients with uncomplicated rhabdomyolysis and a normal first creatinine who can hydrate themselves orally.
Rhabdomyolysis EvidenceBased Management
Establish appropriate admission and discharge criteria for rhabdomyolysis; Standardize inpatient management of rhabdomyolysis; 1) an increase of serum creatinine by ≥ 0.3 mg/dl (≥ 26.5 μmol/l). The diagnostic criteria for aki include any one or more of the following: This suggests that otherwise healthy patients with uncomplicated rhabdomyolysis and a normal first creatinine who can hydrate themselves orally.
Rhabdomyolysis WCH Medicine Blog
Standardize inpatient management of rhabdomyolysis; The diagnostic criteria for aki include any one or more of the following: Establish appropriate admission and discharge criteria for rhabdomyolysis; This suggests that otherwise healthy patients with uncomplicated rhabdomyolysis and a normal first creatinine who can hydrate themselves orally. 1) an increase of serum creatinine by ≥ 0.3 mg/dl (≥ 26.5 μmol/l).
Rhabdomyolysis Treatment Algorithm
This suggests that otherwise healthy patients with uncomplicated rhabdomyolysis and a normal first creatinine who can hydrate themselves orally. 1) an increase of serum creatinine by ≥ 0.3 mg/dl (≥ 26.5 μmol/l). Standardize inpatient management of rhabdomyolysis; The diagnostic criteria for aki include any one or more of the following: Establish appropriate admission and discharge criteria for rhabdomyolysis;
UK Trauma Protocol Manual Rhabdomyolysis (Rhabdo) Diagnosis and Treatment
The diagnostic criteria for aki include any one or more of the following: This suggests that otherwise healthy patients with uncomplicated rhabdomyolysis and a normal first creatinine who can hydrate themselves orally. 1) an increase of serum creatinine by ≥ 0.3 mg/dl (≥ 26.5 μmol/l). Standardize inpatient management of rhabdomyolysis; Establish appropriate admission and discharge criteria for rhabdomyolysis;
UK Trauma Protocol Manual Rhabdomyolysis (Rhabdo) Diagnosis and Treatment
Standardize inpatient management of rhabdomyolysis; The diagnostic criteria for aki include any one or more of the following: Establish appropriate admission and discharge criteria for rhabdomyolysis; This suggests that otherwise healthy patients with uncomplicated rhabdomyolysis and a normal first creatinine who can hydrate themselves orally. 1) an increase of serum creatinine by ≥ 0.3 mg/dl (≥ 26.5 μmol/l).
Emergency Medicine Educationrhabdo chart
Standardize inpatient management of rhabdomyolysis; The diagnostic criteria for aki include any one or more of the following: This suggests that otherwise healthy patients with uncomplicated rhabdomyolysis and a normal first creatinine who can hydrate themselves orally. 1) an increase of serum creatinine by ≥ 0.3 mg/dl (≥ 26.5 μmol/l). Establish appropriate admission and discharge criteria for rhabdomyolysis;
Rhabdomyolysis EMCrit Project
The diagnostic criteria for aki include any one or more of the following: This suggests that otherwise healthy patients with uncomplicated rhabdomyolysis and a normal first creatinine who can hydrate themselves orally. Standardize inpatient management of rhabdomyolysis; Establish appropriate admission and discharge criteria for rhabdomyolysis; 1) an increase of serum creatinine by ≥ 0.3 mg/dl (≥ 26.5 μmol/l).
Standardize Inpatient Management Of Rhabdomyolysis;
Establish appropriate admission and discharge criteria for rhabdomyolysis; The diagnostic criteria for aki include any one or more of the following: This suggests that otherwise healthy patients with uncomplicated rhabdomyolysis and a normal first creatinine who can hydrate themselves orally. 1) an increase of serum creatinine by ≥ 0.3 mg/dl (≥ 26.5 μmol/l).